- ۹۵/۱۲/۲۹
- ۰ دیدگاه
MVVM Overview
Angular is an implementation of MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) design pattern.
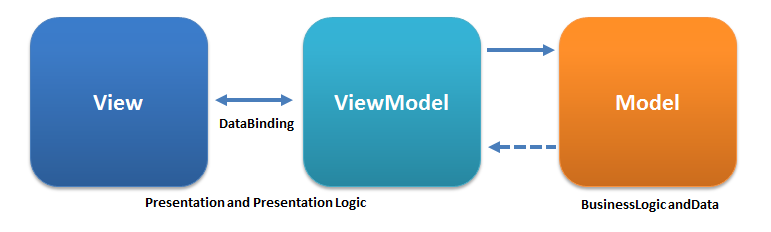
MVVM is different from MVC because it allows for two-way data binding between the model and the view. For example, an input field could be modified by a user, which will cause the data in the model to change, or a change within the model can cause the input data to reflect different data instead.
Model
* The model is the source of data, or the data itself.
* Usually encapsulated in Services, Factories, or Constants in Angular.
View
* The view is what the user sees and interacts with.
* Angular provides a dynamic view on the web page.
ViewModel
* The view-model binds the data from the model to the view and vice versa.
* In Angular, it is encapsulated by the $scope variable, which is decorated by a funtion called a Controller.
Controllers Overview
Controllers are a JavaScript constructor function. They control the view-model contained within the Angular scope.
Angular invokes the controller with a $scope object. The role of controllers in Angular is to expose data to our view via $scope, and to add functions to $scope that contain business logic that enhances view behavior.
Usages
1. Set the initial state of scope variable.
2. Add behavior to scope by two-way binding variables and declaring scope functions.
3. Set up communications to and from view and model through dependency injection.
Creating a Controller
var app = angular.module("app", [])
.controller("myController", [
"$scope",
function($scope) {
// do work here
}
]);We can use ng-controller="myController" in HTML:
<body ng-controller="myController"> ... </body>We can also nest them and create separte scopes which are shared by means of scope:
<body ng-controller="pageController">
<div ng-controller='myChildController'>
<div ng-controller='evenDeeperController'>
</div>
</div>
</body>In order to avoid collision, we can use controller as:
<body ng-controller="SettingsController1 as settings">
{{settings.sampleScopeVariable}}
</body>Scope Overview
$scope is used to make the model available to the view. It is also referred to as the view-model.
Properties
To define Scope variables, simply assign them as subproperties of the $scope object.
var app = angular.module("app", [])
.controller("myController", [
"$scope",
function ($scope) {
$scope.name = "aName";
}
]);Scope properties can be any standard JS objects.
$scope.person = {
firstName: "fName",
lastName: "lName"
};Methods
For adding a method that your view can use:
var app = angular.module("app", [])
.controller("myController", [
"$scope",
function ($scope) {
$scope.title = "Home";
$scope.renameTitle = function (newValue) {
$scope.title = newValue;
};
}
]);Or:
var app = angular.module("app", [])
.controller("myController", [
function ($scope) {
$scope.title = "Home";
function renameTitle(newValue) {
$scope.title = newValue;
}
$scope.renameTitle = renameTitle;
});In HTML:
<div ng-controller='myController'>
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<a href='#' ng-click='renameTitle("Away")'>Click This to Change</a>
</div>* For two-way dynamic binding you should use ng-model:
<textarea class="form-control" ng-model="model.specialInstructions"></textarea>Week One Week Two Week Three Week Four Week Five